There are many medical and social problems in the modern world that are unpredictable and have a specific course, one of which is the disease of civilization - psoriasis. The disease occurs in 1. 5-2% of the population in progressive countries, is prevalent in both men and women, and occurs regardless of the age of the patient.
What is psoriasis or psoriasis?
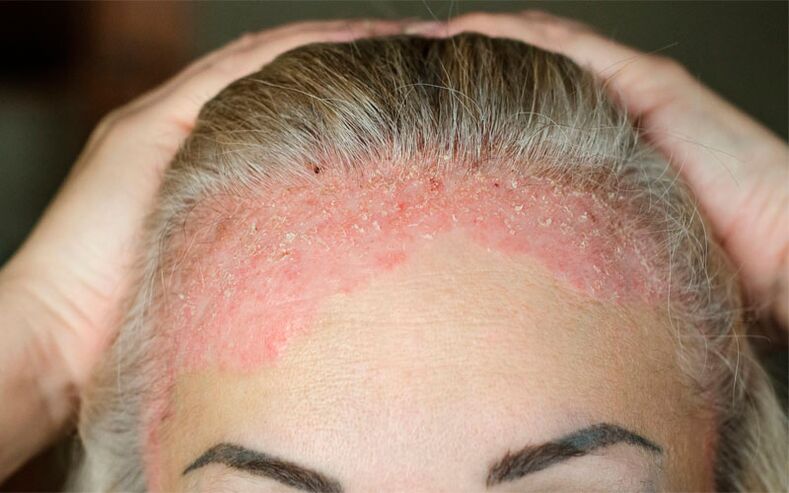
Psoriasis or psoriasis is a genetically determined skin pathology based on a chronic, recurrent inflammatory process in the skin (impaired maturation of keratinocytes) caused by trigger factors. The localization of the rash is extremely diverse, with the location of psoriasis foci occurring on both the oral mucosa and scalp, the extensor surfaces of the limbs, the nails, or the entire body.
As psoriasis is a systemic disease, the lesion will also affect the cardiovascular, nervous, musculoskeletal and other systems. In addition, the manifestation of the disease in 80% of cases is the loss of the scalp in the initial stage, so in this article we want to pay special attention to the specific localization of psoriasis.
Causes of psoriasis on the head
There are 2 types of psoriasis: early and late. The early type is genetically determined, and heredity plays a significant role here. The presence of the disease is known to increase the risk of psoriasis in one child by 14% in one parent and by 40% in both parents.
There are more than 100 factors in the occurrence of scaly lichen, the most common of which are:
- genetic
- viral
- infectious (tonsillitis) and allergic
- stressful (psychosomatic)
- endocrine
- metabolic disorders (lipids, enzymes)
- immune system disorders.
Symptoms of psoriasis of the scalp
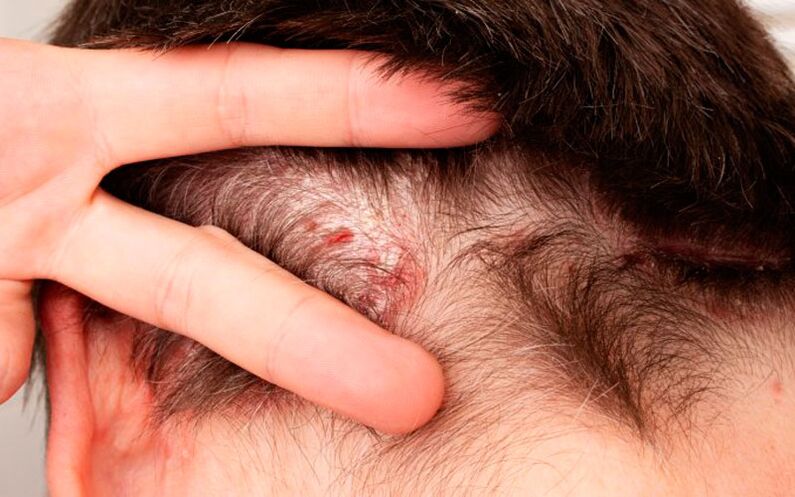
A characteristic feature of psoriasis is a symmetrical flat rise above the skin surface with even rounded borders and increased roughness, as well as a number of easily removable silver scales. The size of the rash can vary from 1 mm to 2 cm, so the formations often fuse to form plaques of different configurations that can reach 10 cm or even 20 cm.
A common occurrence in psoriasis is the so-called "psoriatic crown" - the transition of tumors to the smooth skin of the neck or temple along the hairline. It is a pronounced symptom that is common in patients with scalp psoriasis.
Psoriasis is defined by three main symptoms (Triassic psoriasis):
- "Stearinfol" - a psoriatic plaque is scraped off with a glass plate, causing the scales to thin, which enhances the snow-white color of the surface and resembles a drop of frozen stearin.
- "Terminal film" - with a further scraping a smooth, transparent surface is observed.
- "Blood dew" - the presence of small droplets of blood when scraping.
Developmental stages of psoriasis
The psoriasis process consists of 3 consecutive stages:
- I am progressive
- II standing
- III regressive
Progressive stage
It is characterized by the formation of new papules of increased diameter. The exfoliation process does not extend to healthy areas of the skin while leaving a narrow pink stripe on the edge of the plaques. The main symptom in patients is itching. In addition, the progressive or acute stage of psoriasis is characterized by the presence of Koebner's phenomenon - the formation of new papules 7 days after skin injury. There is a triad of symptoms in psoriatic.
Stationary
At this stage, new elements of the rash do not appear, the itching is reduced or disappears completely. Diagnosis of the psoriasis triad is problematic and Koebner's symptom is negative.
Decreasing
In the regression phase, exfoliation decreases, plaques disappear, but hypopigmented spots form. No symptoms of psoriasis are observed. It is worth noting that even after the regression phase, "obligatory plaques" remain in the scalp, knees, and elbows.
Stages of the disease depending on the degree of damage

Depending on the area of the lesion, there are 3 stages of psoriasis:
- mild - less than 3% of the affected area
- moderate - incidence of papular rashes 3-10%
- severe - the lesions are located on more than 10% of the skin.
How to cure psoriasis on the head
There are various combined methods of pharmacological and non-pharmacological treatment for psoriasis that aim to minimize lesions, improve a patient’s quality of life, and reduce the incidence of relapses.
The treatment for psoriasis depends on the extent of the skin lesions, the shape and age of the patient. If there are additional pathologies in the organs and systems, they are corrected. Patients prescribe a diet that includes limited salt, fatty and fast carbohydrate-rich foods.
Medical therapy
Effective tools for the systemic treatment of psoriasis include:
- desensitizer (30% sodium thiosulfate solution),
- sedatives (valerian infusion, sedatives),
- antihistamines,
- diuretic,
- vitamins (A, B1, B12, B6, E, C),
- hepatoprotectors,
- pyrogenic preparations,
- immunostimulatory drugs,
Short-acting corticosteroids (triamcinalone) are prescribed in the acute common form of psoriasis as well as in erythroderma.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (diclofenac sodium, voltaren, nimesulide) are indicated for damage to the musculoskeletal system (joints).
Cytostatics (metatrexate, azathioprine) are used to treat complex forms of psoriasis.
In severe forms of psoriasis (index greater than 15 units), cytostatics, sedatives, and aromatic retinoids are added to therapy. Glucocorticosteroids are used in critically complex episodes of scalp psoriasis.
In mild cases of psoriasis (PASI index up to 15 units), hyposensitizing drugs, detoxifying and antihistamines, and hepatoprotective agents are used.

The application of topical treatment depends on the stage of the scaly lichen:
- progressive - 1-2% salicylic ointment, corticosteroid creams and ointments
- standing - 5 - 10% naphthalene ointment, 3% salicyl ointment, 2 - 5% sulfur-tar ointment, chamomile main baths
- regressive - 3-5% salicylic ointment, 10-20% naphthalene ointment, 5-10% sulfur tar ointment, psorkutan
Mercury-salicylic ointment, lotion and shampoo Psoriks, Tar balm, preparations containing zinc are widely used in scalp psoriasis. Hot baths once every 2-3 days are also an integral part of the treatment of the disease. In the winter form of psoriasis, the therapy is based on the use of ointments in combination with ultraviolet radiation.
Non-pharmacological treatment
Medications are not the only basis for treating psoriasis. The use of phototherapy methods also contributes to rapid healing and the onset of remission.
There are the following types of radiation exposure:
- Photochemotherapy (PUVA therapy) is a type of light therapy that is combined with the use of photosensitizers. The mechanism lies in the fact that it emits ultraviolet radiation on the surface of the skin to treat complex forms of psoriasis.
- Selective therapy is more effective in treating exudative and simple forms of psoriasis with a small number of rashes. The process of therapy consists of 20-30 times, the efficiency is 80%.
- Narrowband therapy - when used in the presence of superficial psoriasis, the rays do not penetrate deep into the skin balls, but only have a superficial effect. The purpose of the procedure is to prevent malignant degenerative processes in the cells.
- Narrow-spectrum UVB treatment - This type of therapy significantly reduces the incidence of side effects such as redness and burns. The procedure is performed 20-30 times, it can be used only in case of skin changes.
In addition, the bath treatment has a positive effect. Known sources of healing are Lake Kunigunda, the Crimean coast, the Black Sea and the Dead Sea.
Experimental methods
Scientists are not stopping and are still looking for new, effective ways to treat psoriasis, which include the following.
Plasmapheresis
A gentle poisoning procedure that helps cleanse blood plasma of pathogenic ingredients and toxins. After a procedure, up to 30% of the blood is usually emptied. This manipulation is used in severe and complex cases of psoriasis. The process of plasma aphoresis takes place in 3-6 sessions, with a one-week break.
The mechanism of this procedure is as follows: certain membranes filter the intercellular fluid and return it to the bloodstream, while the beneficial components are retained as much as possible and the pathogenic toxic substances are destroyed.
Cryotherapy or "cold treatment"

The therapy of the disease is due to the effect of ultra-low degrees on the body. The sharp effects of cold help to activate the immune system and stimulate metabolism in general. This procedure has a complex effect on the whole body and focuses on local, skin lesions.
It is important to keep in mind that cryotherapy is not suitable for all patients. Due to the anatomical features of the location of the blood vessels, some individuals experience cramps, swelling, and sharp dilation of the vessels, resulting in disturbed blood circulation. In addition, some patients may be sensitive to allergic reactions such as cold hives.
Effects of cryotherapy:
- increases the body's defenses
- improved regeneration processes
- the negative symptoms disappear: itching, burning, peeling
- improves metabolism in the skin
- extension of remission periods.
Immunobiological preparations
These are protein-based products that have a direct effect on the immune system and prevent the occurrence of concomitant diseases. In the presence of a psoriatic process, the body is constantly replenished due to an excessive amount of TNF protein. These drugs block the effects of TNF-α, reducing the symptoms of the inflammatory process in psoriasis.
Ozone therapy
A new, effective way to treat psoriasis. Ozone is known to be detoxifying, anti-inflammatory, antiplatelet and immunomodulatory. The benefits of ozone therapy are ease of use, rapid effectiveness, complete lack of side effects.
Characteristics of psoriasis treatment in children and adolescents

It should be noted that psoriatic disease is less common in children than in adults. The explanation is the low detection rate of psoriasis, frequent, frequent regression cases, and significant remission periods of up to 12 years.
The clinical picture of psoriasis in children is characterized by frequent changes in the skin under the hair. Girls get sick twice as often as boys, which is linked to endocrine diseases that occur during adolescence. Children are characterized by a pronounced picture of the pathological process (significant inflammation and varying degrees of itching).
The symptoms of psoriasis in children under 10 years of age are different from those in adults. The localization of the rash occurs at atypical sites, such as on the face, back of the head, genitals, or deeper sections of the skin under the skin. The causative mechanism of the disease is often acute infection (influenza, pneumonia), psycho-emotional stress.
In most children, the first signs of lesions appear on the scalp and are accompanied by redness, peeling of scales. Hair loss is not uncommon in the most severe cases of scalp psoriasis.
Therapy for childhood psoriasis is based on the use of medicinal ointments and creams, used in combination with other drugs in severe episodes. This approach makes it possible to reduce the negative manifestations of the disease and contributes to rapid recovery.
How to treat psoriasis on the head at home

In the fight against psoriasis, various base creams, body lotions, herbal shampoos and water-based emulsions are used to fight dry scalp, which not only relieve the symptoms of dermatitis, but also relieve the symptoms of psoriasis.
The most popular home remedies for psoriasis are creams, salicylic ointments and specialty shampoos.
Creams
Use non-hormonal agents based on natural ingredients. The active ingredients can be varied, the most common of which are:
- zinc - quickly eliminates dehydration and inflammation of the skin, has antiseptic properties, has an antibacterial effect
- Vitamin D - treats simple forms of psoriasis, relieves unpleasant symptoms such as peeling and itching, and promotes regeneration
- urea and naphthalene - has a tonic and soothing effect on the skin
- herbal extracts - have antiseptic properties, eliminate hypersensitivity and exacerbation of the inflammatory process
- floralizin - promotes rapid healing, relieves unpleasant manifestations of psoriasis
- urea and beeswax - suitable for sensitive skin requiring hydration and nourishment, restores the protective layer
Salicylic ointment in the fight against psoriasis
Salicylic acid obtained from willow bark is the active ingredient in salicylic ointment and has anti-inflammatory and regenerating properties. The advantage of salicylic ointment over hormonal drugs is the absence of side effects.
Positive properties of salicylic ointment:
- fights inflammation - removes itching and redness
- antiseptic effect - eliminates pathogenic microorganisms
- keratoplastic effect - prevents the formation of purulent foci, promotes the regeneration process.
- destroys the horny substance - exfoliates the bark.
Salicylzinc ointment is also widely used in the treatment of psoriasis and is no less effective.
Shampoos
The following types of shampoos are available to treat psoriasis of the scalp:
- Birch tar based. Tar helps to gently cleanse the skin from the stratum corneum, impurities, eliminates itching and burning, has antifungal properties.
- Antifungal - the main active ingredient in ketoconazole eliminates the growth of fungal infections and promotes the healing of skin wounds.
- Contains salicylic acid, ketoconazole, zinc. This spray shampoo eliminates the inflammatory process, softens the skin and has an antiseptic effect.
- Healing. Normalizes the secretion of fat under the skin, strengthens hair, relieves inflammation.
It is also important to note that when washing your hair with psoriasis, use only warm water, not hot. The use of hair dryers, curlers and ironing should be minimized.
Folk remedies for the treatment of psoriasis

Lotions based on celandine, aloe vera, chamomile, apple cider vinegar are excellent for treating psoriasis. A bandage moistened with solution is placed on the lesions. This procedure reduces inflammation, kills pathogens and improves metabolism in the skin.
Kefir and mud masks, which also work as part of traditional medicine, are no less effective. Such masks also moisturize the hair, have an anti-inflammatory effect and improve blood circulation to the scalp.
Which product is better?
To treat psoriasis of the scalp, it is advisable to use mild, gentle, odorless products. Regular cleansing and hydration for proper hair and skin care is the basis of psoriasis. It is important that the products used contribute to the normalization of the nutrient balance, the restoration of the affected areas of the skin, the preservation of the pH of the scalp and the hydration of the stratum corneum of the epidermis.
All these effects, and even more, are typical of the products of the Fitomarket web store. Here you can not only choose the most appropriate tools and methods for high-quality treatment of psoriasis of the scalp, but also get the right advice on the right medications for you.
F. A. Q
Can Psoriasis Be Cured With Zinc Ointment?
Zinc ointment has an anti-inflammatory, disinfecting and covering effect, it promotes the formation of a protective layer on the skin surface. If the affected areas are lubricated daily with zinc ointment, the positive effect will occur quickly, but this drug will not be able to completely cure psoriasis, as the treatment must be complex.
Can Scalp Psoriasis Be Cured With Hydrogen Peroxide?
Hydrogen peroxide performs mechanical cleansing by releasing active oxygen and removes harmful substances from damaged skin, but as with zinc ointment, this component alone does not cure psoriasis.
Is psoriasis contagious?
Psoriasis does not spread because it is not contagious, so it is not worth avoiding contact and communication with people with the disease.
Is Scalp Psoriasis Dangerous?
Without treatment, psoriasis can lead to serious complications and even death. Keep in mind that psoriatic lesions can spread to the deep layers of the skin as well as other organs and systems of the body (nails, cardiovascular system, musculoskeletal system, etc. ).
How to distinguish psoriasis from dermatitis
It is known that seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp never affects smooth skin and is characterized by a lack of infiltration process, in contrast to seborrheic psoriasis, which forms a "psoriatic crown" and moves to smooth areas of the skin of the forehead and neck. . Also noteworthy is the hereditary factor in the incidence of psoriasis.